Everything you should know about AC Adapter
In our increasingly connected world, electronic devices have become indispensable tools for work, communication and entertainment, and at the heart of powering these devices is the AC adapter, also widely known as a power adapter, wall charger or power brick. This unassuming yet vital external power source helps convert alternating current (AC) from a standard wall outlet into direct current (DC), the form of electrical energy required to operate most modern electronic devices. Whether it’s a compact “wall adapter” that plugs directly into an outlet, or a plug-in “power brick” with a detachable power cord, these devices are ubiquitous and integral to our digital lives.
The conversion process inside an AC adapter is a marvel of electrical engineering. When the adapter is plugged into an electrical outlet, it precisely converts high-voltage AC power to the low-voltage DC power required to operate a device or charge its internal battery. In the past, this conversion relied on bulky linear power supplies that used large transformers to step down the voltage, rectifiers to convert to pulsating DC, and filters to smooth the waveform.
However, the field of power conversion has undergone a quiet revolution. Modern AC adapters are primarily powered by switch-mode power supplies (SMPS), which have achieved significant leaps in efficiency, compactness, and weight reduction. SMPSs operate at higher frequencies, allowing for smaller transformers and significantly reducing energy losses. From linear to SMPS to today’s gallium nitride (GaN) technology, this continued technological advancement is not just about reducing physical size, but also about the relentless pursuit of greater energy efficiency and less heat. Less heat directly translates to increased reliability and lifespan for both the charger itself and the electronic devices it powers. This underlying trend directly benefits consumers through more compact, safer, and more durable products, often without consumers explicitly realizing the complex engineering involved.
AC adapter do more than simply provide power; they are an integral enabler of modern electronic design and user experience. Computers and many other electronic devices require a stable, regulated, low-voltage DC power source to operate properly and charge batteries.
External adapters offer several distinct advantages over integrating power directly into a device.
First, they improve safety by converting hazardous 120V or 240V mains power to lower, safer voltages at the wall outlet before reaching the user-operated device. This design isolates hazardous voltages outside the device enclosure, which is especially important for devices with lightweight enclosures that might otherwise expose internal electronic components.
Second, external AC adapter help reduce heat. By removing heat-generating power conversion components from the host device, the reliability and life of sensitive internal electronic components are significantly improved.
Third, they help reduce electrical noise. Converting potentially noisy AC line power to “clean,” filtered DC and keeping it a safe distance from noise-sensitive circuits via an external adapter effectively reduces radiated electrical noise.
Fourth, for portable devices such as laptops, offloading power components to an external adapter can significantly reduce carrying weight and size, directly improving device portability.
Finally, external AC adapter offer exceptional flexibility, allowing devices to be powered from a variety of mains voltages (e.g., 120 VAC or 230 VAC) or even vehicle/aircraft batteries simply by using different adapters.
The inherent safety advantage of external AC adapter goes beyond simply protecting against electrical hazards; it fundamentally enables more innovative and compact device designs. By physically isolating bulky, hot, and high-voltage power conversion circuits, manufacturers are free to design electronic devices that are lighter, thinner, and more aesthetically pleasing. This creates a powerful positive feedback loop: the necessity of external adapters promotes thinner device form factors, which in turn reinforces the need for more compact and efficient external power solutions. The connection between technical functionality and tangible user benefits, such as enhanced device portability, streamlined aesthetic design, and overall improved product reliability and user experience, underscores the critical importance of these external power solutions.
AC vs. DC Charging: Demystifying the Current Flow
Understanding the fundamental difference between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) is essential to understanding modern charging technology. AC is characterized by a cyclical change in direction, with both voltage and current constantly fluctuating between positive and negative values. It is the standard for powering homes and most commercial buildings around the world. In contrast, DC flows in a constant, unidirectional path with consistent polarity. Most electronic devices, including laptop adapter and smartphones, use a DC power source for internal power.
Beyond Laptops: Devices Suited for AC adapter
AC/DC adapters are essential external power sources for a wide range of electronic devices that cannot draw power directly from the grid or do not have enough internal space to accommodate bulky AC/DC conversion components. While laptop chargers and cell phone chargers may be the most common AC/DC adapters, their uses extend far beyond personal electronics.
The Evolution of Power: From Linear to Switched-Mode and GaN Technology
The evolution of laptop power adapters reflects the ongoing quest for efficiency and miniaturization. Early AC/DC adapters were based on linear power supply designs, which featured a bulky transformer that stepped down the mains voltage, then converted it to pulsating DC through a rectifier, and finally smoothed the waveform through a filter. While these designs were fully functional, they were large, heavy, and inefficient. In the early 21st century, switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) became widely used. SMPSs became almost mainstream in AC adapter due to their small size, light weight, and significantly higher efficiency than linear designs (typically up to 80-90%). SMPSs operate at higher frequencies, allowing for smaller transformers and significantly reducing energy losses. SMPS technology is now widely used in applications such as laptop chargers, battery chargers, automotive, LED lighting, and other consumer electronics.
A major advancement in the early 2020s was the adoption of gallium nitride (GaN) to replace traditional silicon transistors in switching wall adapters. This innovation has resulted in smaller chargers that are more efficient, safer, and run cooler. GaN’s ability to handle higher currents without overheating allows for faster charging and the ability to charge multiple devices simultaneously. This has enabled compact wall adapters to power not only smartphones and tablets, but even high-performance laptops. The development of GaN chargers was initially delayed by their high cost, but the need for fast charging has accelerated their adoption. GaN chargers come in a variety of output powers: 65W, 140W, 240W, 300W, 500W, in a compact form factor, and often feature multiple USB-C and traditional DC ports for versatile charging.
Decoding Laptop AC Adapter Specifications: Voltage, Amperage, and Wattage
Understanding the electrical specifications of your laptop charger is critical for compatibility and safety. The wattage of a laptop charger refers to its power rating, which indicates how much power it can provide to a laptop. The basic calculation is to multiply the output voltage (V) by the output current (Amps).
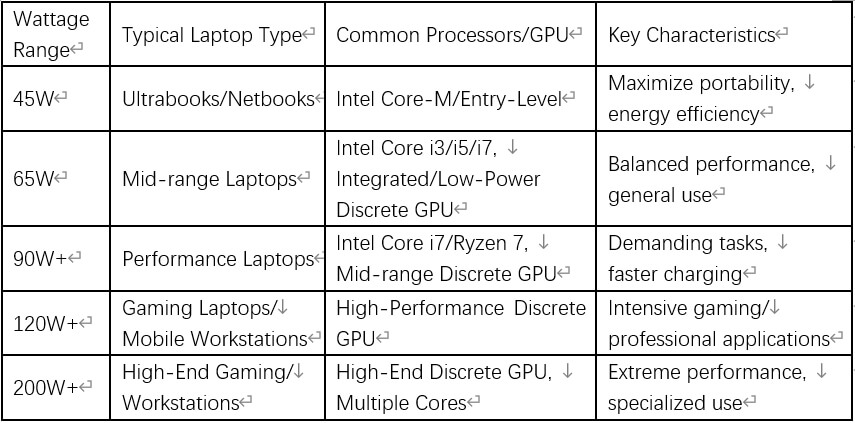
Laptop AC Adapter Come In Various Wattages,
generally ranging from 40 to 150 watts, but a high-performance gaming laptop or mobile workstation may require 200W or more.
- 45W Chargers: These are commonly used for smaller, lighter laptops, such as ultrabooks and netbooks, designed for low power consumption, often featuring energy-efficient processors.
- 65W Chargers: This represents the average laptop charger wattage and is typically found with mid-range laptops that have moderate power consumption. These chargers can handle the power needs of laptops utilizing standard processors (e.g., Intel Core i3, i5, or i7 series, or AMD Ryzen processors) and often integrated graphics or low-power discrete GPUs. A 60W or 65W charger is generally sufficient for most standard laptops.
- 90W, 120W, 150W, or 200W+ Chargers: These higher-wattage power adapters are specifically designed to support laptops that require more power for enhanced performance and faster charging times. This category includes high-performance gaming laptops or mobile workstations equipped with power-hungry components.
A critical compatibility rule is that it is generally safe to use a charger that is much higher than the laptop requires. For example, it is perfectly safe to charge a 65W laptop with a 100W charger, especially now that the USB Power Delivery (USB-PD) standard is prevalent. In addition, if the laptop’s internal charging circuitry specifically supports fast charging at higher power, it will charge faster, otherwise using higher power will not necessarily reduce charging time. Conversely, using a laptop charger with a power lower than the specified value may cause a variety of harmful problems: significantly slower charging speeds, reduced performance (the laptop may throttle the CPU to save power), overheating of the adapter, and even possible damage to the laptop due to insufficient voltage or current, especially when the laptop is in use. The general rule is that high-power chargers are generally safe, while low-power chargers are harmful. So when faced with uncertainty, it is safer to choose a slightly higher power (provided that other compatibility factors such as voltage and connector type are met) than to risk insufficient power and potential damage.
The output wattage (e.g., 65W, 90W, 120W) is almost always indicated on the AC adapter‘s label. It is equally critical to verify the output voltage (V) and amperage (A) on this label, as these must precisely match a device’s input requirements.
Table 1: Common Laptop AC Adapter Wattages and Their Applications
Connector Types: Ensuring a Perfect Fit
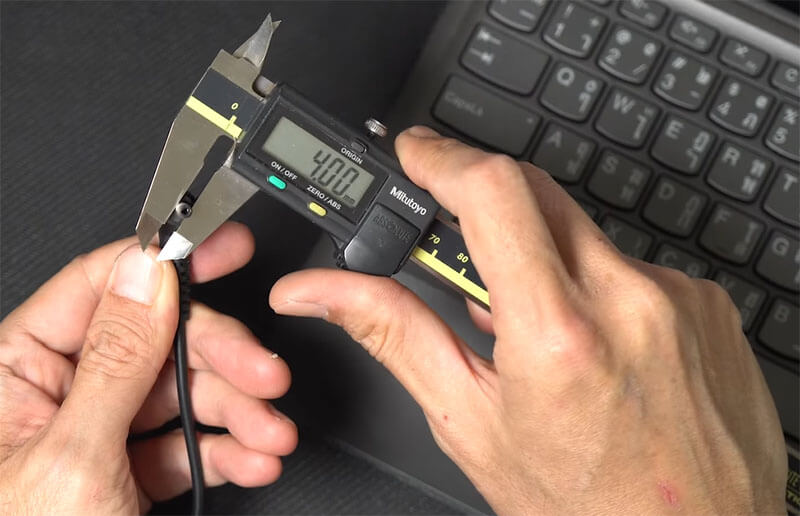
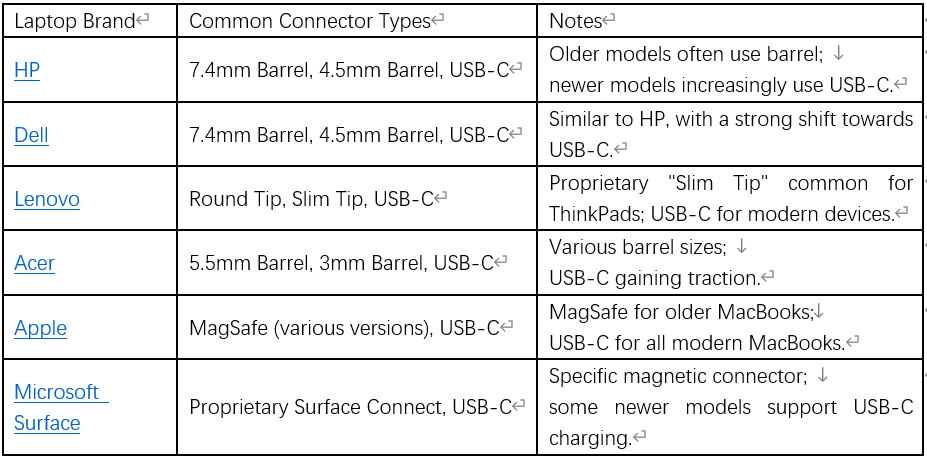
Laptop chargers come with a diverse array of connector (pin) types, and selecting the precisely correct one is absolutely crucial for ensuring compatibility and proper function. An incorrect connector will simply not fit or could damage the port. Historically, many laptop brands have utilized their own specific barrel connector sizes, defined by their Outer Dimension, Inner Dimension, and sometimes a Center Pin Size.
Examples of common proprietary connectors include:
- HP: Frequently uses sizes like 7.4mm and 4.5mm.
- Dell: Also commonly uses 7.4mm and 4.5mm.
- Lenovo: Features “Round Tip” and “Slim Tip” connectors.
- Acer: Common sizes include 5.5mm and 3mm.
- Toshiba: Uses adapters such as “G” (4.0 x 1.7 mm) and “C” (5.5 x 2.5 mm), and sometimes a larger “B” (6.3 x 3.1 mm).
The rise of USB-C and Power Delivery (USB-PD) is rapidly changing the laptop charger landscape and is becoming a universal standard due to its many benefits. The USB-C connector is designed to be bidirectional, which avoids the problem of devices not working or being damaged when plugged in incorrectly. USB-C ports, especially those that support Power Delivery (USB-PD), can deliver a powerful power of up to 100W, and even up to 240W according to the latest PD 3.1 standard. This versatility means that USB-C supports both power delivery and data transfer, making it an extremely adaptable port. Many modern laptops from brands such as Apple (MacBook), Chromebook, Dell, HP, Lenovo, Asus, Acer, and Samsung now feature USB-C as the primary charging port.
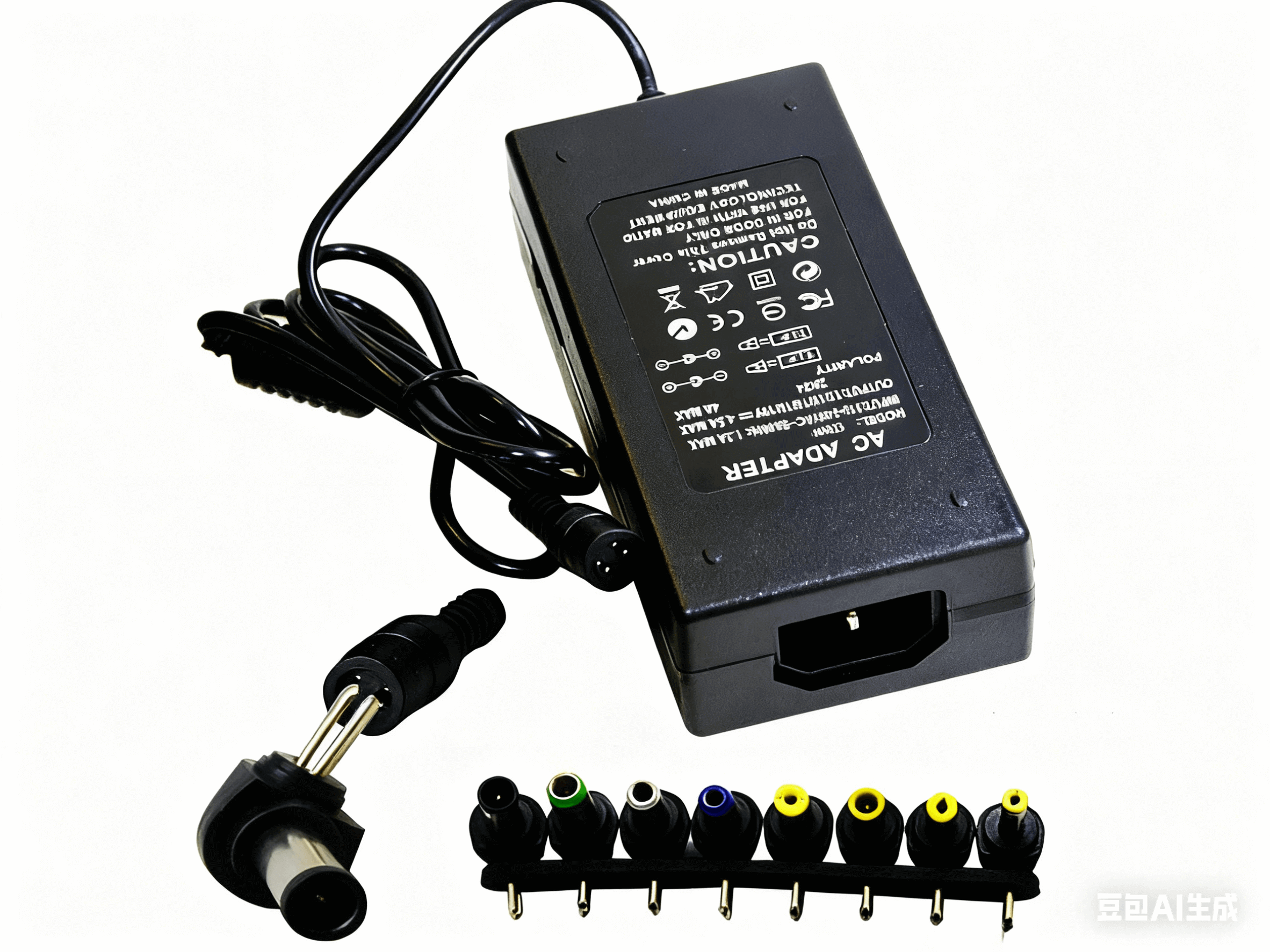
Universal laptop chargers often come with multiple interchangeable plugs to fit a variety of laptop models. While this provides convenience and versatility, some universal plugs may not fit well with certain models, and not all universal chargers include a USB-C connector. An often overlooked but critical factor is the polarity of the AC adapter connector. This polarity (center positive vs. center negative) must exactly match the power input or charging port on the device. Most power adapters use a center positive connector, indicated by a specific symbol or +/- sign.
Table 2: Common Laptop Adapter Connector Types by Brand
Built-in Safeguards: Essential Safety Features of Quality AC Adapter
A high-quality AC adapter should incorporate several built-in safety features to protect both the connected device and the user from electrical hazards and damage. These protections are critical for reliable and safe operation.
- Overvoltage Protection (OVP): This feature prevents damage to the equipment by automatically shutting down or regulating the output if the voltage from the power supply exceeds a safe threshold, guarding against power surges.
- Overcurrent Protection (OCP): Designed to prevent damage from excessive current draw, OCP limits the output current if it exceeds a predefined safe level.
- Short-Circuit Protection (SCP): If a circuit is shorted due to misconfiguration or damage, this critical protection feature automatically shuts down the circuit to prevent damage, overheating, or potential fire hazards.
- Overheating Protection (OTP) / Temperature Control: This feature prevents the adapter from reaching dangerously high internal temperatures. While it is normal for an AC adapter to get warm during use due to energy conversion, excessive heat can indicate internal issues or a malfunction. Modern technologies like GaN inherently help reduce heat generation, contributing to cooler and safer operation.
Choosing the Right Replacement Laptop Adapter: A Buyer’s Guide
Using an incompatible charger can have serious consequences, including damaging your laptop’s battery, voiding its warranty, and even creating a fire hazard, so a thorough compatibility check is crucial.
Step-by-Step Compatibility Check: Matching Your Device’s Needs
- Identify your laptop model and the part number of your original charger: Check the label on your current charger to find its part number (usually listed as “P/N,” or “FRU”). Also, find the serial number or model number on the bottom of your laptop. Use this number to look up a recommended replacement laptop charger on the manufacturer’s website.
- Verify voltage, current, and power requirements: Carefully check the “Output” section on the original AC adapter’s label, which lists its voltage (V), current (A), and power (W). The replacement charger’s output voltage and current must exactly match the device’s input requirements. The voltage, current/power, and connector type all need to be an exact match. Any deviation, especially in voltage or physical fit of the connectors, can cause immediate failure or long-term damage to the laptop.
AC Charger.AC Adapter 1 - Confirm Connector Type and Size: Make sure the replacement connector is an exact match. If you’re considering a universal charger, verify that it includes a plug specifically for that model and that it’s securely inserted. Pay attention to polarity (center positive or center negative), which is usually indicated by a diagram or +/- symbol on the adapter’s label.
AC Charger.AC Adapter 2 AC Charger.AC Adapter 4
Ensuring Authenticity and Quality: The Importance of Certification
When purchasing any AC adapter, especially a laptop replacement adapter, it is critical to verify its certification and quality through proper certifications. These certifications guarantee that the product meets specific safety, performance, and environmental standards.
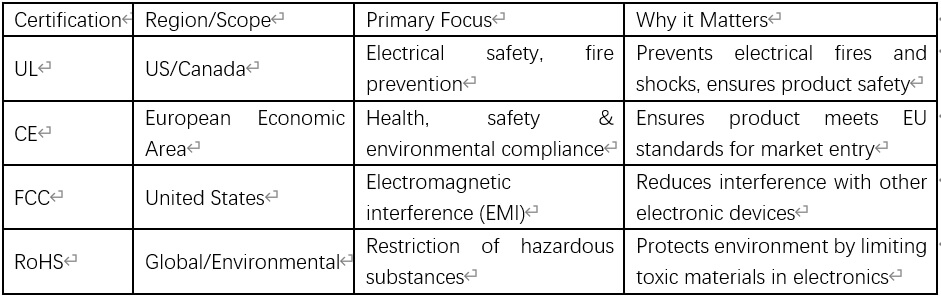
The main certifications include:
- UL (Underwriters Laboratories): A critical safety certification primarily recognized in the United States and Canada. UL certification ensures that the product has been tested and meets UL’s safety requirements, primarily concerned with preventing electrical fires and other safety hazards.
- CE (Conformité Européenne) Marking: Required for the majority of products marketed within the European Economic Area. The CE mark is a manufacturer’s declaration that the product complies with the health, safety, and environmental protection requirements of applicable EU directives. It is conceptually similar to a combination of UL and FCC certifications.
- FCC (Federal Communications Commission): This certification primarily regulates electromagnetic interference (EMI) in the United States. FCC certification ensures that electronics meet relevant standards for electromagnetic interference. Class B certification is more stringent and is for consumer products.
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): This directive, originating in the EU but widely adopted globally, restricts the use of specific hazardous materials (such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and certain flame retardants) in electrical and electronic equipment. RoHS compliance promotes environmental safety and responsible manufacturing.
Table 3: Key Safety Certifications for AC Adapters
Choose the right charger for your laptop
The market for laptop AC Adapter is broadly divided into two main categories:
- Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs): These are the primary laptop manufacturers themselves, such as Dell, HP, Apple, Lenovo, Acer, Microsoft, and Asus, who produce their own branded laptop chargers. OEM chargers are typically designed and optimized specifically for their respective models, and using the original manufacturer’s adapter is often recommended for guaranteed optimal performance, compatibility, and to maintain warranty validity.
- Third-party manufacturers: In addition to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), there is a strong market for third-party manufacturers to provide compatible or universal laptop chargers. These manufacturers often offer universal chargers with multiple interchangeable contacts that work with a wide range of laptop models and provide a versatile solution for users with a variety of devices. So you may have two choices: OEM chargers offer the highest compatibility guarantees and are generally considered higher quality, but they can be more expensive and have strict brand restrictions. Conversely, universal chargers from third-party manufacturers are more feature-rich and generally cost less. This is a trade-off that users must choose carefully based on their priorities.
Choosing a reliable manufacturer’s products to power your valuable electronic devices is essential. HTJ International Co., Limited is a manufacturer specializing in laptop battery and laptop charger. Its extensive laptop AC adapter product catalog covers many major laptop brands and specifications to ensure wide compatibility. It also provides excellent quality, professional technology, and customer-oriented service.
HTJ’s products cover a wide range of wattages (e.g. 30W, 35W, 45W, 65W, 90W, 100W-150W, 150W-200W, 200W+) and multiple connector types (e.g. 5.5×1.7mm, 4.5×3.0mm Blue Port, USB-C, USB Slim, 7.4×5.0mm) to ensure a perfect fit for a variety of devices. The extensive and specific product list covers a variety of major laptop brands, wattages, and connector types, demonstrating its ability to serve a highly diverse market and is your trusted laptop battery and adapter partner.
Conclusions & Recommendations
AC adapter are much more than simple power cords; they are sophisticated power conversion devices that are critical to the operation and lifespan of modern electronic devices, especially laptops. The evolution from bulky linear power supplies to efficient switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) to today’s compact, high-power GaN chargers highlights the ongoing drive for greater portability, safety, and performance. It’s critical to understand key specifications such as voltage, amperage, and wattage, and ensure they match the device requirements precisely. While high-wattage chargers are generally safe, using lower-wattage chargers can cause serious performance issues or even damage the device. While connector types are increasingly trending toward USB-C, careful attention still needs to be paid to ensure physical compatibility and correct polarity.
When choosing a laptop charger, you have different options: OEM products (compatibility and warranty are guaranteed) and stable and reliable third-party chargers (with diverse features and often integrated cutting-edge technologies such as GaN). No matter which product you choose, it is essential to verify the authenticity of the product through recognized safety certifications such as UL, CE, FCC and RoHS. These certifications are the most reliable indicators for consumers to judge product safety, quality and environmental compliance, which can directly reduce potential economic losses and safety risks.
For consumers seeking reliable and high-quality laptop power solutions, HTJ International Co., Limited presents a compelling option. With a history dating back to 2012, a dedicated focus on laptop battery and AC adapter, and extensive in-house manufacturing capabilities, HTJ demonstrates a strong commitment to product integrity. Their comprehensive product range, covering major laptop brands, diverse wattages, and connector types, ensures broad compatibility. Furthermore, the presence of essential certifications like CE, RoHS, and FCC on their products underscores their adherence to international safety and environmental standards. Choosing HTJ International Co., Limited means investing in products with expertise, strict quality control, and a customer-centric philosophy that gives you peace of mind that your valuable device is supported.